Understanding the 3rd Conditional in English
Introduction:
What is the 3rd Conditional?
Short Explanation: The 3rd conditional is used to talk about hypothetical situations in the past that didn’t happen. It reflects on how things could have been different if a past event had occurred differently.
Example situation:
“Maria was running late for an important job interview because she didn’t set her alarm the night before. She rushed out the door without eating breakfast, forgot her resume, and got stuck in traffic. As a result, she arrived late, feeling flustered, and the interview didn’t go well.“
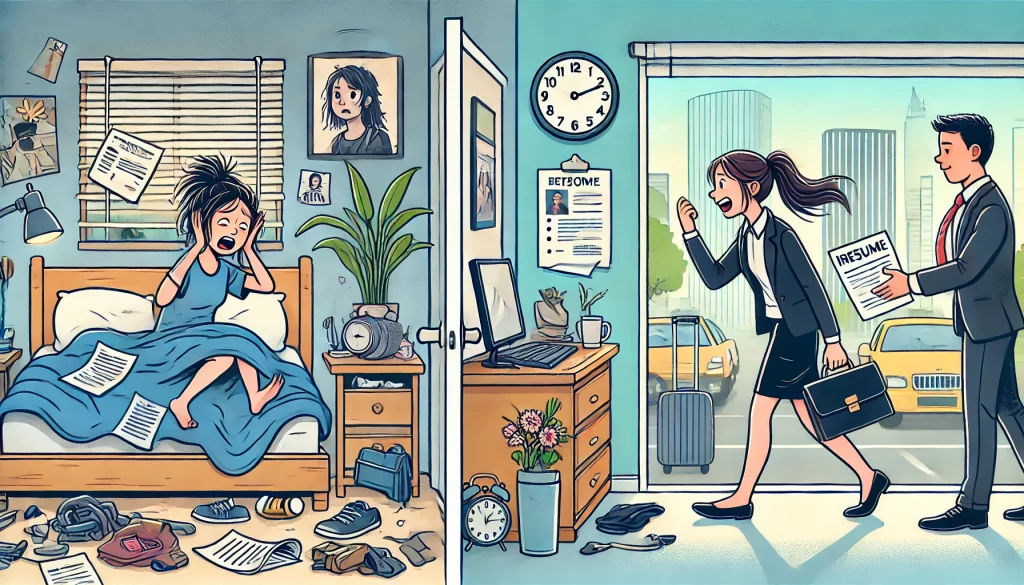

What Maria could have done differently:
- If Maria had set her alarm, she would have woken up on time.
- If she had prepared her resume the night before, she would have brought it to the interview.
- If she had left earlier, she would have avoided the traffic.
- If she had eaten breakfast, she would have felt more focused and calm.
These changes could have helped Maria make a better impression at the interview, potentially leading to a different outcome.
Section 1: Formula of the 3rd Conditional
Formula:
- If + Past Perfect, + would have + past participle
Example:
- If I had known about the event, I would have attended.
- If he had studied for the test, he would have passed with flying colors.
- If they had booked their tickets earlier, they would have gotten better seats.
- If we had taken an umbrella, we wouldn’t have gotten wet in the rain.
- If she had apologized, they would have forgiven her.
Short Explanation:
- “If” Clause: The first part of the sentence uses the past perfect tense (had + past participle).
- “Result” Clause: The second part uses “would have” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Section 2: Function of the 3rd Conditional
Short Explanation: The 3rd conditional is used to imagine different outcomes in the past. It’s often used to express regret, relief, or to consider alternate realities.
Example:
- Regret: If she had studied harder, she would have passed the exam. (She didn’t study, and she didn’t pass.)
- Relief: If I had taken that job, I would have been miserable. (I didn’t take the job, and I’m glad.)
- Frustration: If he had left earlier, he would have caught the flight. (He didn’t leave early, and he missed the flight.)
- Gratitude: If she hadn’t taken that risk, she wouldn’t have started her own business. (She took the risk, and now she’s grateful for her success.)
- Disappointment: If they had booked the tickets sooner, they would have gone to the concert. (They didn’t book in time, and they missed the concert.)

Section 3: Examples of 3rd Conditional in Use
Affirmative Example:
- If we had left earlier, we would have avoided the traffic.
Negative Example:
- If he hadn’t eaten so much, he wouldn’t have felt sick.
Mixed Example:
- If they hadn’t booked the tickets earlier, they would have missed the flight.

Short Explanation: Each of these examples imagines a past situation that didn’t happen, emphasizing the consequence that would have followed if it had.
Section 4: Common Mistakes with the 3rd Conditional
Short Explanation: Many learners confuse the 3rd conditional with the 2nd conditional. Remember:
- 2nd Conditional: Talks about unreal situations in the present or future.
- 3rd Conditional: Talks about unreal situations in the past.
Example of Incorrect Usage:
- Incorrect: If she would have studied harder, she would have passed.
- Correct: If she had studied harder, she would have passed.


